Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. PCOS is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including irregular menstrual periods, excess androgen (male hormone) levels, and the presence of small cysts on the ovaries.
The exact cause of PCOS is not known, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Insulin resistance, which affects the body's ability to use insulin effectively, is also often associated with PCOS. This can lead to higher insulin levels in the body, which in turn can stimulate the ovaries to produce excess androgens.
The symptoms of PCOS can vary from person to person, but commonly include:
Irregular periods: Women with PCOS may have infrequent, prolonged, or absent menstrual periods.
Excess androgen levels: Elevated levels of androgens can lead to symptoms such as acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness.
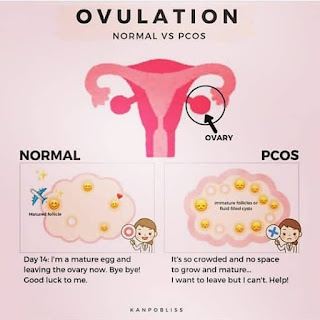
Ovarian cysts: The ovaries of women with PCOS may have multiple small cysts, which are follicles that have not matured properly.
Weight gain: Many women with PCOS experience weight gain or have difficulty losing weight.
Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance is associated with PCOS and can lead to increased insulin levels and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Fertility problems: PCOS is a common cause of female infertility due to irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation.
The diagnosis of PCOS is usually made based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and various tests, including blood tests to measure hormone levels and ultrasound imaging to assess the ovaries.
While there is no cure for PCOS, the symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight management. Medications may also be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve insulin sensitivity. Treatment plans are typically tailored to the individual's specific symptoms and goals, such as managing fertility or managing symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
If you suspect you may have PCOS or are experiencing any concerning symptoms, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management options.



Comments
Post a Comment